Star's Graphic:
http://clips.thestar.com.my.s3.amazonaws.com/Interactive/highrise/highrise.mp4
Only 74 out of 7,325 high-rise residential properties in Peninsular Malaysia earned the top five-star ranking in an evaluation of their property management standards. And more than half are below par, earning only one and two stars.
IT is one thing to be a developed state by 2020. But it is another thing entirely to have a developed state of mind – and Malaysians have a long way to go to achieve that.
Take, for instance, condominium- and apartment-living.
Some of these properties may come with top notch facilities but when it comes to managing their upkeep, there is much to be desired.
Or so says the latest findings on the quality of managing stratified properties from a survey by the Urban Wellbeing, Housing and Local Government Ministry.
Every year, the ministry conducts its Strata Scheme Management Quality Evaluation, or “Star Rating”, which ranks the standards of joint management bodies (JMBs) or management corporations (MCs) of apartments and condominiums.
These bodies are ranked based on how they do in seven areas (see graphic below for details); five stars is the highest rank.
But, as it turns out, more than half – or 69% – of condominiums and apartments nationwide ranked “below par”, scoring only one and two stars in 2015. In 2014, a slightly smaller percentage, 65%, were ranked below par.
Only 1% – or 74 – out of 7,325 strata development schemes surveyed earned five stars in the 2015 ratings, made available to Sunday Star.
If such a trend continues, future residents will inherit poor standards of living amidst modern facilities.
Currently, almost six million Malaysians out of 20 million city folk are living in stratified buildings like apartments and condominiums.
“But this number is expected to rise in future as the country progresses and becomes more urbanised,” says Mohammad Ridzwan Abidin, Urban Wellbeing, Housing and Local Government Ministry urban service division under-secretary.
He says one of the major problems that condo dwellers continue to face is the refusal of other residents to pay maintenance fees. Other problems are building defects and matters involving enforcement.
“For now, about 70% of residents are at a level where they are merely aware of what needs to be done in managing their property. They are not yet at a level to appreciate the benefits of cooperating with each other and creating a better living culture,” he says.
Mohamad Ridzwan says there is a need to change the mindset of people to foster more civic-minded communities in high-rise buildings.
“Future generations will likely live in stratified buildings, so people should try to set a proper precedent for them,” he says.
He points out that there are also more people moving out of landed properties and into high-rise buildings.
“This group of people will have to learn to adapt to the culture of living in stratified buildings as it is different from living in houses.
“They will need to be more inclusive of and cooperative with their neighbours,” he says, adding that they would also have to learn to be more considerate when it comes to using shared facilities.
Stressing that it all boils down to the mindset of residents, Mohamad Ridzwan highlights the case of Rumah Pangsa Orkid, a low-cost flats property in Ulu Tiram, Johor, which made it into the Malaysia Book Of Records in 2014 for obtaining the ISO 9001:2008 standard for exemplary management.
“Until today, they remain the only low cost flat development to have achieved this,” he says, adding that there are yet to be any high-end condominiums accorded the same standard.
Mohamad Ridzwan says the ministry will continue to actively educate dwellers on proper management of their properties.
“We will embark on more education programmes to promote better practices through advertisements in the mass media,” he says.
On the Strata Management Tribunals to hear disputes, Mohamad Ridzwan says four such tribunals have been successfully set up to cover different zones in Peninsular Malaysia.
“Since their formation the tribunals have heard about 200 cases per month,” he says.
In March, Sunday Star reported that residents who do not pay maintenance fees and other charges were set to face the music, with the Government forming a team to strengthen the enforcement of the Strata Management Act.
The Act also enables residents to take their disputes to a Strata Management Tribunal to settle matters.
Building Managers Association of Malaysia committee member Richard Chan agrees that the “biggest and most critical” problem is the collection of fees, saying that it is rare that JMBs or MCs are able to collect payment from 80% of residents.
“It is more common for the collection rate to be at 40% or 50%,” he says.
Chan laments that petty excuses are often given by residents to defend their refusal to pay up.
“Some refuse because they don’t use the facilities.
“When people ask why they don’t want to pay, they simply say they don’t swim or play tennis,” he shares.
Chan adds that many unit owners live elsewhere or are based overseas and so are reluctant to pay.
“Some are not satisfied with services like garbage collection and defy orders to settle the fees,” he says.
He urges future condo owners to refrain from buying properties that come with all sorts of facilities if they are unwilling to pay up.
“Sometimes, it isn’t about whether they can afford the fees or service charges. It is about their attitude and mentality.
“Some don’t pay simply because their neighbours are not paying and are getting away with it,” Chan says, adding that such attitudes have resulted in some apartments owing up to RM200,000 in water and electricity bills.
The lack of money in the sinking fund also hinders JMBs and MCs from paying for major works like repairing lifts.
“It becomes a vicious cycle. Because people are not satisfied with the upkeep of the place, they do not pay the fees.
“But when they do not pay, there isn’t enough funds for upkeep,” he says.
Also, developers must do their part by informing all potential property buyers of the exact amount of all service charges, says Chan.
“Developers will try to promote their projects for more sales but they should also inform buyers of the fees they are expected to pay.
“Owners should also consider that, after a year, the fees may go up as warranty periods for equipment expire,” he says.
Federation of Malaysian Consumers Associations secretary-general Datuk Paul Selvaraj says many complaints against MCs have been made to the federation.
“High-end condominiums are generally better managed. We received a lot of complaints from people in medium cost apartments,” he says.
He says that consumers and the building management should both be more responsible.
“Consumers need to settle payments that they have agreed to. But they should also be receiving good service in return, like efficient rubbish collection,” he says.
Selvaraj highlights that the only way forward is for management bodies and residents to have a good working relationship.
“People should understand that managing their building is a collective responsibility.
“More dialogues should be held on how to improve the community to ensure good quality of life wherever we live,” he adds.
by Yuen Meikeng The Star/Asia News Network
More professionalism needed in managing high-rises
WITH more high-rises mushrooming, a Building Managers Board is urgently needed, according to Tan Sri Teo Chiang Kok, deputy president of the Building Managers Association of Malaysia (BMAM).
BMAM is an umbrella body comprising stakeholder organisations representing management corporations (MCs), joint management bodies (JMBs), chambers of commerce, developers, engineers, architects, shopping and high-rise complex managers, and managing agents.
Appealing to the Urban Wellbeing, Housing and Local Government Ministry to set up the board urgently, Teo says such a body is long overdue.
“Millions of stratified properties are coming up. Building management is becoming a very big industry. We have to start regulating. All building managers must be registered and regulated,” he says.
To date, some 600 building managers have voluntarily registered with the association, he shares, estimating that there are probably tens of thousands more.
Meanwhile, the BMAM is focused on educating its members and interested parties on good management via collaborations with institutions of higher learning.
Describing building management as a multitasking, multidiscipline function that attracts people from various backgrounds and with a variety of skills, Teo says that basic criteria for the role is needed. A Building Managers Board, once set up, will have guidelines and regulations to bring professionalism to the role.
Persons deregistered by the board cannot be hired as property managers, he suggests. This, he feels, will make hiring building managers cheaper while ensuring that they are monitored.
“So long as they fulfil the board’s requirements, anyone can be a building manager. The board will monitor and weed out the errant ones. JMBs and MCs can hire cheaper, smaller companies, even individuals, to manage their buildings if they don’t have the budget.”
Urban Wellbeing, Housing and Local Government Ministry urban service division undersecretary Mohammad Ridzwan Abidin acknowledges the proposal to set up a Building Managers Board.
“However, no decision can be made by the ministry yet as this matter is still being discussed,” he says.
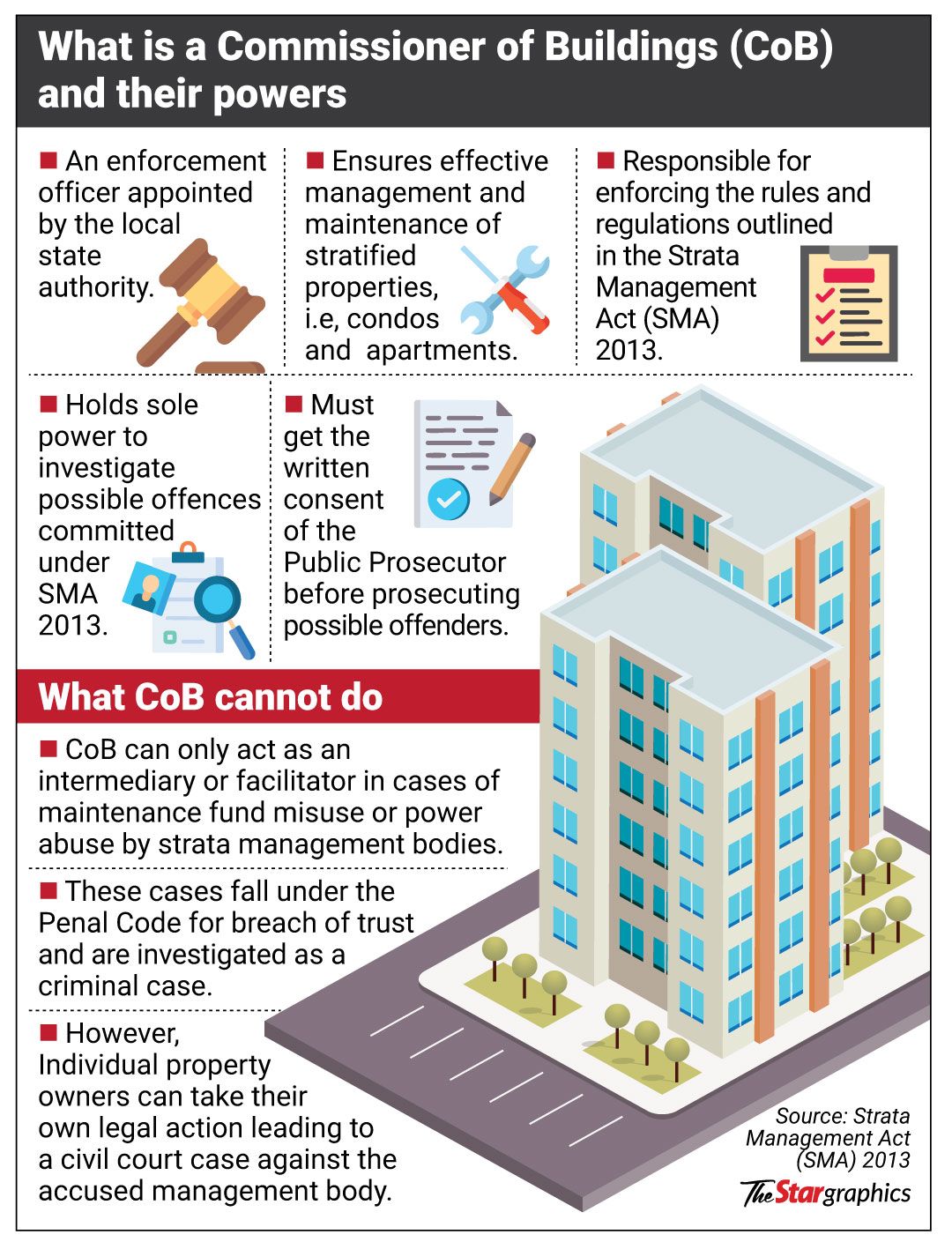
He says the ministry issued a directive to Commissioners of Buildings nationwide last month to register all managing agents to protect residents from unscrupulous parties.
The BMAM would also like to see the country’s 150-plus Commissioners of Buildings (COB) given proper funding and staff. The role of the commissioner is mostly undertaken by local council heads or mayors, which isn’t right because they already have so much on their plate, he says.
The Commissioner of Buildings must be a dedicated, full-time position supported by an adequately funded department. Now, it’s mainly a one-man show, he observes.
“The Act is a good tool,” he says, referring to the Strata Management Act 2013, “But it’s for the COB to implement it efficiently. An effective COB can nip many things in the bud – the COB can call a unit owner, find out the grouses and give directives. If the COB can offer easy resolution, a lot of problems will be solved.”
Apart from supporting the position of COB, JMBs and MCs must familiarise themselves with the Strata Management Act, says Richard Chan, a committee member of the Building Managers Association of Malaysia and a past president of the Malaysian Association for Shopping and High-Rise Complex Management.
“For instance, many aren’t aware that money collected should go to JMBs and MCs – not the companies or individuals hired to manage the property. What if these companies don’t pay the service contractors?”
On Tuesday, a full-day strata management seminar will be held at Wisma Rehda in Petaling Jaya, Selangor, to explain the Act, he says, urging stakeholders to attend the event.
Teo feels that the Act is too harsh on JMB volunteers. Calling it a thankless job, he says it’s difficult getting residents to even attend AGMs, what more serve on the JMB.
“Despite not being paid, JMB members risk personal liability actions. It’s too onerous. It’s overkill because there are already laws like the Penal Code which imposes fines and jail terms.”
And he feels that the Act places too many obstacles in front of willing volunteers.
“The JMB chairman and members can only serve for two and three years respectively. Such restrictions will make things worse because as it is, no one wants the job. Our solution is to extend the chairman’s term to three years; but if at the AGM there’s no one else who wants the post, he or she should be allowed to stay on. And members should be permitted to stay on for as long as they want.” - The Star
Related articles:
 PETALING JAYA: From run-down facilities and dirty walkways to allegations of misused management funds, the issue of poor property and building management continues to plague stratified homes in Malaysia.
PETALING JAYA: From run-down facilities and dirty walkways to allegations of misused management funds, the issue of poor property and building management continues to plague stratified homes in Malaysia. PETALING JAYA: From run-down facilities and dirty walkways to allegations of misused management funds, the issue of poor property and building management continues to plague stratified homes in Malaysia.
PETALING JAYA: From run-down facilities and dirty walkways to allegations of misused management funds, the issue of poor property and building management continues to plague stratified homes in Malaysia.









 Booming demand: With millions of stratified properties coming up, building management is becoming a very big industry. —Reuters
Booming demand: With millions of stratified properties coming up, building management is becoming a very big industry. —Reuters
